An in-depth guide to thermal transfer printing
Share
Thermal transfer printing is a widely used technology in the world of printing and labeling. It's known for its versatility, durability, and ability to produce high-quality prints on various materials. This guide will delve into the intricacies of thermal transfer printing, from the basic principles to advanced techniques and considerations.
Contents
- An introduction to thermal transfer printing
- Key terminology & concepts
- What is thermal transfer printing?
- Types of ribbons
- Choosing the correct ribbon
- Getting a great print output
- Typical applications
- Future trends
1. An introduction to thermal transfer printing
What is thermal transfer printing?
Thermal transfer printing is a digital printing method that involves the transfer of ink from a ribbon onto a substrate using controlled heat. Unlike direct thermal printing, which uses heat-sensitive paper, thermal transfer printing offers more durable and long-lasting prints. It is commonly used for labeling, barcode printing, product packaging, and various industrial applications.
Types of thermal transfer printing
There are two primary types of thermal transfer printing:
- Flat head: In this method, the print head is in direct contact with the substrate and ribbon, making it suitable for a wide range of materials.
- Near edge: Here, the print head is at a slight angle to the substrate and ribbon, allowing for higher printing speeds and precision. Near-edge printing is often used in high-speed packaging applications.
Key terminology & concepts
- Print head: The print head is a critical component responsible for generating heat and transferring the ink from the ribbon to the substrate. It consists of an array of tiny heating elements that can be individually controlled to create text, graphics, or barcodes.
- Ribbon: The ribbon is a roll of coated material that carries the ink. It is made of either wax, wax-resin, resin, of specialty materials, depending on the application requirements.
- Substrate (material): The substrate refers to the material on which printing is done. It can vary widely and includes paper, film, fabric, plastic, and more. The choice of substrate influences the type of ribbon and print settings needed.
- Platen roller: The platen roller is responsible for maintaining even pressure between the print head, ribbon, and substrate. It ensures consistent and high-quality printing.
What is thermal transfer printing?
Thermal transfer printing operates on the principle of selectively heating the print head elements to melt the ink on the ribbon. When the heated elements come into contact with the ribbon, the ink transfers onto the substrate, forming the desired image or text.
The diagram below shows how the ink transfers onto the media:
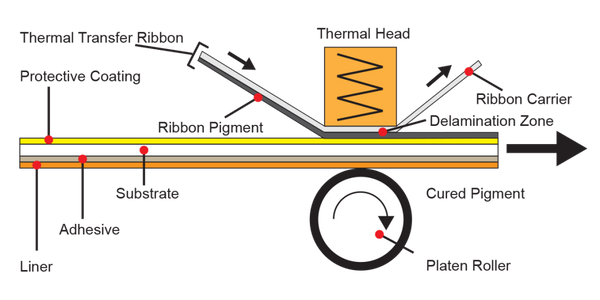
Heat transfer mechanism
The heat generated by the print head melts the ink on the ribbon, allowing it to transfer to the substrate. The quality and durability of the print depend on factors like temperature, pressure, and ribbon-substrate compatibility.
Printing resolution and quality
Thermal transfer printers can achieve high-resolution prints, making them suitable for applications where image clarity and detail are essential. Printing quality can be further enhanced by selecting the appropriate ribbon and substrate combination.
Types of ribbons
Wax ribbons
- Wax ribbons are the most common and cost-effective option.
- They are suitable for printing on paper and some synthetic materials.
- Ideal for applications where durability is not a primary concern.
Wax-resin ribbons
- Wax-resin ribbons offer better durability and resistance to smudging and abrasion.
- They are suitable for printing on a wider range of materials, including paper and synthetic labels.
- Commonly used for barcode and product labeling.
Resin ribbons
- Resin ribbons provide the highest level of durability and resistance to harsh environmental conditions.
- They are used for printing on synthetic materials like polyester and polypropylene.
- Ideal for applications where labels must endure exposure to chemicals, extreme temperatures, or outdoor elements.
Specialty ribbons
- Specialty ribbons include options like colored ribbons, metallic foils, and scratch-off ribbons.
- These are used for specific applications where standard ribbons are insufficient.
Choosing the correct ribbon
Factors to consider
- Durability requirements
- Environmental conditions (indoor, outdoor, chemical exposure)
- Substrate material
- Image quality and resolution
- Budget constraints
Material compatibility
Ensure that the chosen ribbon and substrate are compatible to achieve the desired print quality and durability. Manufacturers often provide compatibility guidelines.
6. Getting a great print output
The thermal transfer printing process can be more susceptible to errors than other print methods. Therefore there are a few parameters we can adjust to ensure a beautiful print quality.
- Temperature control: Adjusting the print head temperature is crucial for proper ink transfer. Temperature settings may need fine-tuning based on the ribbon and substrate used.
- Print speed: Print speed affects throughput. High-speed printing may require adjustments to other settings to maintain print quality.
- Print darkness: Print darkness controls the density of the printed image. It's important for achieving optimal contrast and readability.
- Energy level: Adjusting the energy effectively changes the amount of temperature each individual print head applies to get a smooth ink transfer. Too high and the ribbon carrier will crease and cause something we call striking. Too little and you'll only get partial ink transfer.
7. Typical applications
Because direct thermal printing can be so durable there are a huge range of applications. The key requirement is that the substate being printed is smooth, so it maintains a consistent contact with the print head & ribbon.
Here is a small thermal printer that can be put in-line as part of a larger production process:

- Variable data printing: Thermal transfer printing allows for the easy inclusion of variable data, such as serial numbers, expiration dates, and batch numbers on labels for tracking and traceability.
- Flexible packaging: It's commonly used in the production of flexible packaging materials like stand-up pouches, sachets, and bags, where durability and print quality are essential.
- Barcode printing: This is arguably the most popular use of a thermal printer.
- Retail and inventory management: Thermal transfer printing is a staple in retail for creating barcode labels used in inventory management, pricing, and point-of-sale operations.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, barcode labels are used to track patient records, medications, and equipment, improving patient safety and efficiency.
- Asset tracking: Because of the durability of the ink, thermal printing methods are ideal for asset tracking labels.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturers employ direct thermal printers to label and track the movement and status of equipment and components throughout the production process.
- Logistics and supply chain: Thermal transfer labels are crucial for tracking products in transit, ensuring efficient supply chain management. A thermal transfer printer can be installed 'in-line' so it becomes part of the machine.
- Medical labels: The instant-curing ink and clean process of a thermal printhead makes thermal transfer technology perfect for use in clean rooms and medical facilities.
- Patient ID and wristbands: Thermal transfer printing is used to create durable patient identification wristbands, labels for medical records, and medication packaging in healthcare settings.
- Laboratory labels: Laboratories rely on thermal transfer printing for labeling test tubes, specimen containers, and slides, ensuring accurate sample identification.
- Clothing labels: Thermal transfer is used to print tags and labels for clothing, providing information such as size, care instructions, and branding.
- Accessories and footwear: It's also utilized for labeling accessories, footwear, and other fashion items.
8. Future trends
Sustainability and eco-friendly options
As environmental concerns grow, there's a trend toward developing eco-friendly ribbon materials and substrates. Look for innovations that reduce waste and energy consumption while maintaining print quality.
Integration with industry 4.0
Thermal transfer printers are increasingly integrated into smart manufacturing processes, enabling real-time monitoring and control. This connectivity enhances efficiency and traceability in production.
Enhanced connectivity
Thermal transfer printers are becoming more connected through wireless technologies and cloud-based platforms, allowing remote management, updates, and data sharing.
9. Conclusion
Thermal transfer printing stands as a robust and indispensable technology in the world of printing and labeling. Its enduring popularity is rooted in its versatility, reliability, and capacity to produce high-quality prints on various materials. As a technical professional, understanding the intricacies of thermal transfer printing is paramount to harnessing its potential for a multitude of applications.
Versatility and Reliability: One of the defining attributes of thermal transfer printing is its adaptability. Whether you're tasked with printing labels for retail products, barcodes for inventory management, durable labels for extreme environments, or colorful tags for fashion items, thermal transfer printing offers solutions. Its reliability ensures that once the label or print is created, it endures and remains legible over time.
Quality and Precision: Thermal transfer printing shines when it comes to producing high-resolution prints with sharp details and clear images. This quality is essential for applications where precision and legibility are critical, such as barcode scanning and medical labeling. Understanding the nuances of printer settings, ribbons, and substrates is key to achieving the desired print quality.
Customization and Variable Data: For businesses and industries where each label or tag may carry unique information like serial numbers, dates, or batch codes, thermal transfer printing excels. Its capacity for variable data printing simplifies tracking, traceability, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Maintenance and Efficiency: To maintain the integrity of your thermal transfer printing system, regular maintenance is essential. Printhead cleaning, ribbon changes, and platen roller upkeep are crucial for preventing downtime and ensuring consistent performance.
Environmental Considerations: With increasing environmental consciousness, the industry is moving towards sustainable options. Watch for innovations in eco-friendly ribbon materials and recyclable substrates to minimize waste and reduce the ecological footprint of thermal transfer printing.
Industry 4.0 Integration: The future of thermal transfer printing is intricately tied to Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT). As manufacturing processes become more connected and automated, thermal transfer printers are evolving to offer real-time monitoring and control. This integration enhances efficiency, quality control, and traceability in production.
Enhanced Connectivity: Wireless technologies and cloud-based platforms are making their way into thermal transfer printers, enabling remote management, firmware updates, and data sharing. This enhanced connectivity streamlines operations and provides insights into printer performance and usage.
In conclusion, the world of thermal transfer printing is dynamic and ever-evolving. Technical professionals who dive into its nuances, stay abreast of technological advancements, and adapt their practices accordingly will find this printing technology to be an invaluable asset. As we look toward the future, expect to witness further innovations that make thermal transfer printing even more efficient, sustainable, and seamlessly integrated into the fabric of modern manufacturing and labeling requirements. Embrace these developments, and you'll continue to unlock the full potential of thermal transfer printing in your technical endeavors.