A comprehensive guide to flexographic printing
Share
Flexographic printing, also known as flexo printing, is a versatile and widely used printing method known for its efficiency and the ability to print on various materials.
This comprehensive guide provides an overview of flexographic printing, including its principles, processes, advantages, and applications.
Let's dive in!
Contents
- An introduction to flexographic printing
- The flexographic process
- What materials can flexo print on?
- Common applications
- Environmental impact
- Future trends
- Conclusion
1. An introduction to flexographic printing
Some background
Flexographic printing is a printing technique that employs printing plates to transfer ink onto different materials. It emerged in the century as a more efficient alternative to letterpress printing.
Synthetic rubbers were invented in the 1930s, which made the properties of rubber stamps and plates much more reliable than before.
With this innovation, Mosstype Corporation made huge advances in rubber plate making, allowing effective processes to be developed for aniline printing, which was the precursor to flexography.
It wasn't until 1938 that the International Printing Ink Corporation devised a way of accurately metering the ink transferred to the rubber plate. They used a system inspired by gravure cylinders and called their invention an anilox roller, which is still used today (source).
Key terms
- Flexible printing plate: Flexography utilises plates made of rubber or photopolymer to transfer ink onto the material.
- Anilox roller: A hard cylinder provides the printing plate with a measured amount of ink. An anilox roller is usually made from steel or aluminium coated with chromium oxide powder, whose surface is engraved with millions of very fine dimples, known as anilox cells, where the ink resides before being transferred to the flexo plate.
- Quick drying inks: There are 3 different types of ink used for the flexographic printing process: solvent, water-based, and UV. Solvent-based inks are generally used when printing on film. Water-based inks are printed on paper for corrugated boards and paper containers. UV flexographic inks are used for label application in narrow web printing.
The pros & cons
The advantages of flexo printing are:
- Versatility: It can print on substrates like plastics, paper and labels.
- Speed: Ideal for large print runs due to its high-speed production capabilities.
- Cost effective: Low consumables & ink cost make this printing process very low cost
- Minimal setup time: Quick plate changes help minimize downtime.
The disadvantages of flexo printing are:
- A limited range of colours: It may have limitations in achieving colours and gradients.
- Plate wear and replacement: The printing plates wear out over time and need to be replaced.
- Challenges with fine detail: It might need help with designs or small fonts.
2. The flexographic process
Flexographic printing consists of 3 key stages.
Prepress
Prepress prepares the design so it's ready to be printed. It also creates any associated hardware needed to print the job.
- Artwork preparation: Artwork received from a customer usually requires some editing to get it ready for printing. This could be converting the colours to CMYK, adding a cutline, simplifying the shape, changing the size, or doing something else.
- Layout: Once the artwork file is in order, it needs to be nested to use the material efficiently. Nesting is also often referred to as imposition.
- Creating printing plates: Once the nested file is ready, this is imposed onto the flexible printing plates.
- Mounting plates: After the flexographic printing plate is created, it must be fixed onto the cylinders as part of the machine setup.
Printing
Once everything is ready to go, it's time to start the flexographic printing process.
- Adding ink: Firstly, the operator adds the pre-mixed ink into an ink tray.
- Transferring ink: The anilox roller rotates in an ink tank at high speeds. That fills the tiny dimples of the roller and acts as the transfer from the ink tray to the flexible printing plate. An optional doctor blade scrapes excess ink off the anilox roller to ensure a nice even ink layer.
- Impression cylinder: The substrate is fed in between the rotating flexographic plates and the impression cylinders, which causes the ink to move from the plate to the media.
- Multiple passes for full-colour printing: This process is repeated up to 10 times to create full-colour, high-definition images on the printed media.
Post Press
After printing, a few things need to happen.
- Curing: After printing, the operator needs to ensuring that all printed materials are dry or cured to avoid smudging.
- Finishing: Finishing can involve many different processes. The most typical finishes would be; slitting & rewinding, folding, glueing or even further printing with foils.
- Quality control: The finished products are then thoroughly inspected for any defects or discrepancies in colour accuracy and other issues.
This diagram helps to visually show what happens:
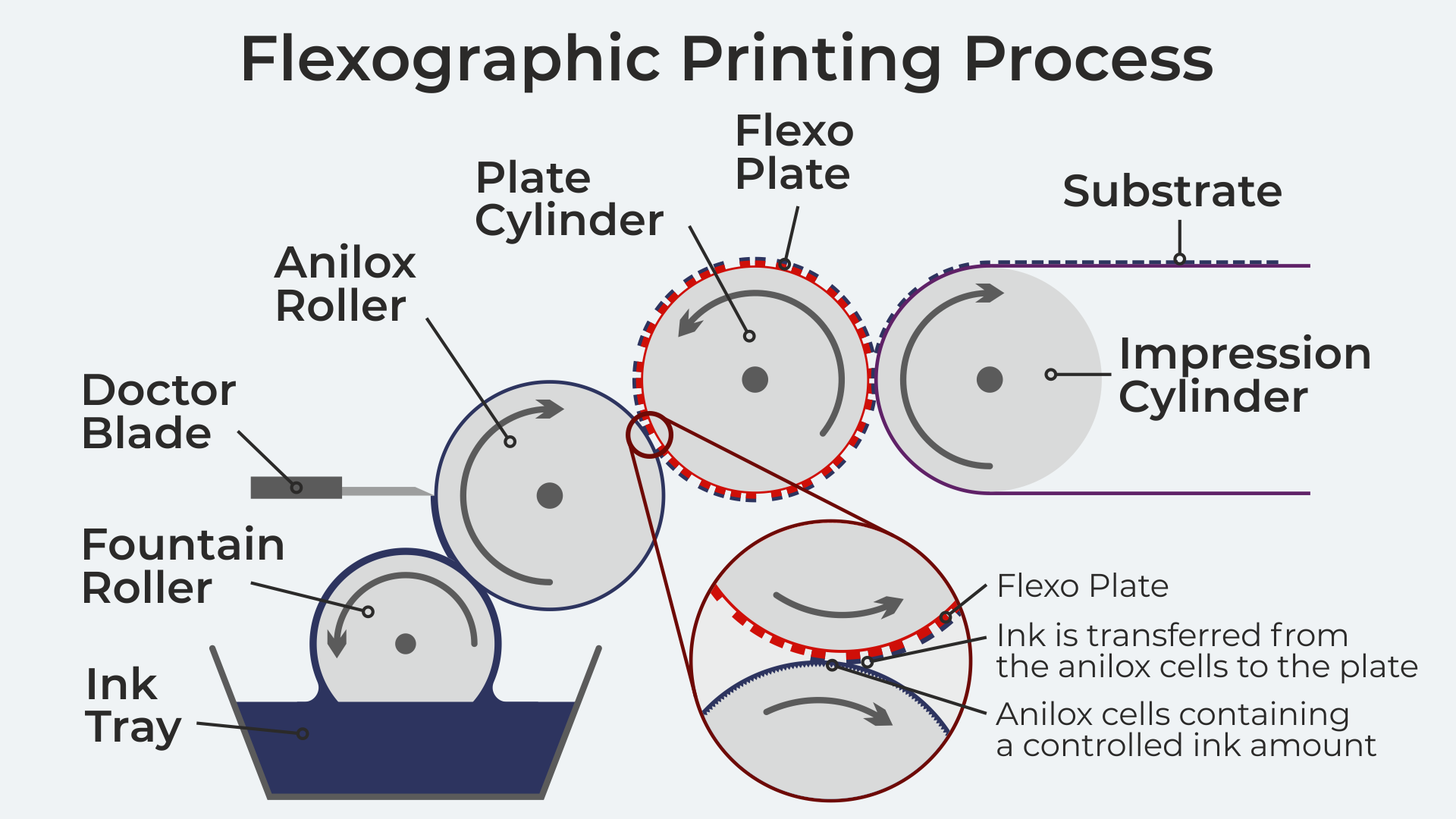
3. What materials can flexo print on?
One of the huge benefits of the flexographic printing process is that due to the flexible plate, it can print on many substrates - even ones that are slightly uneven.
Different formats of printing press are used depending on the media to print. This can be sheet-fed or web-fed. Web-fed machines take big rolls, and typically look like this:
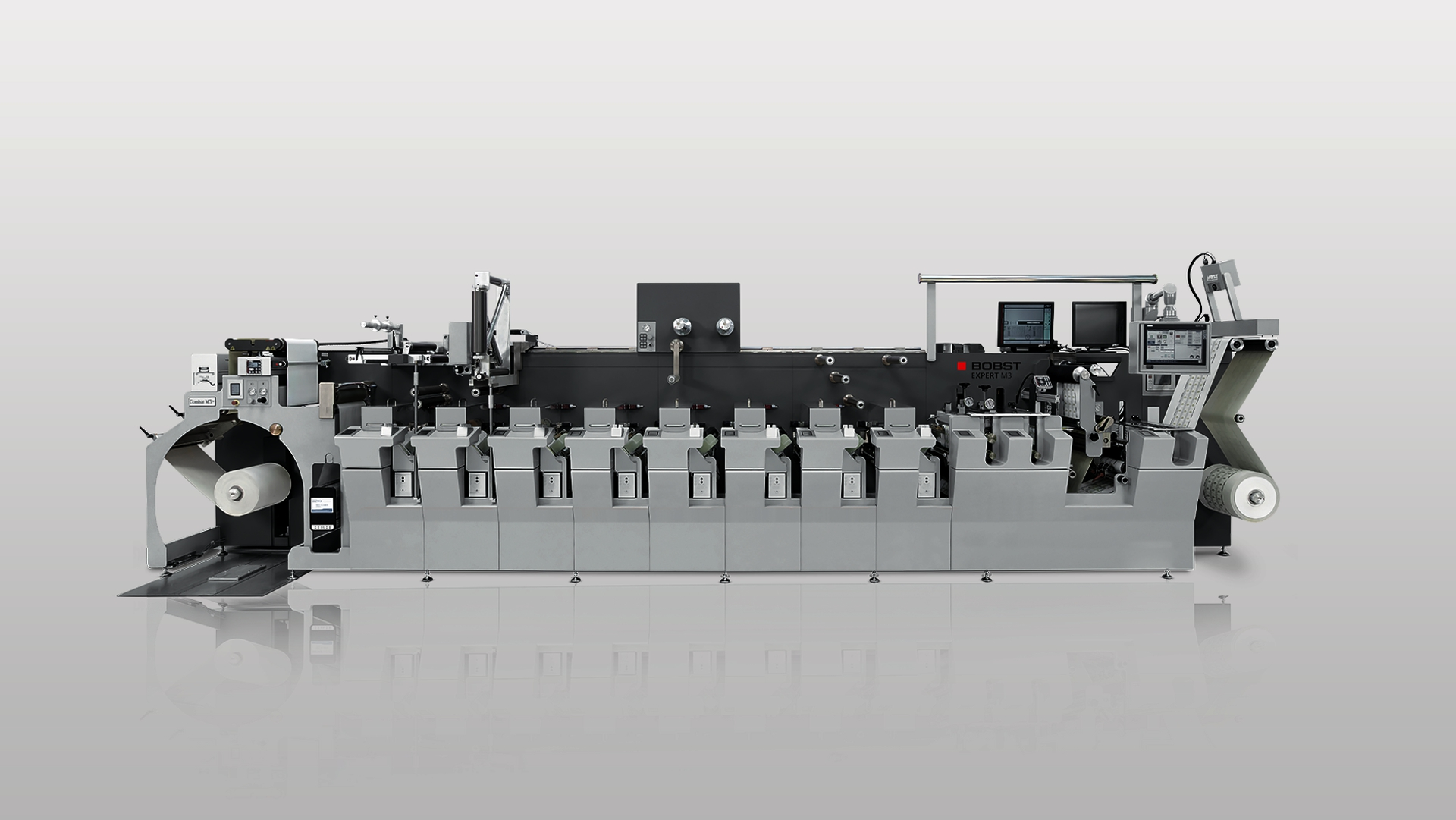
Whereas sheet fed machines look simpler, like this:
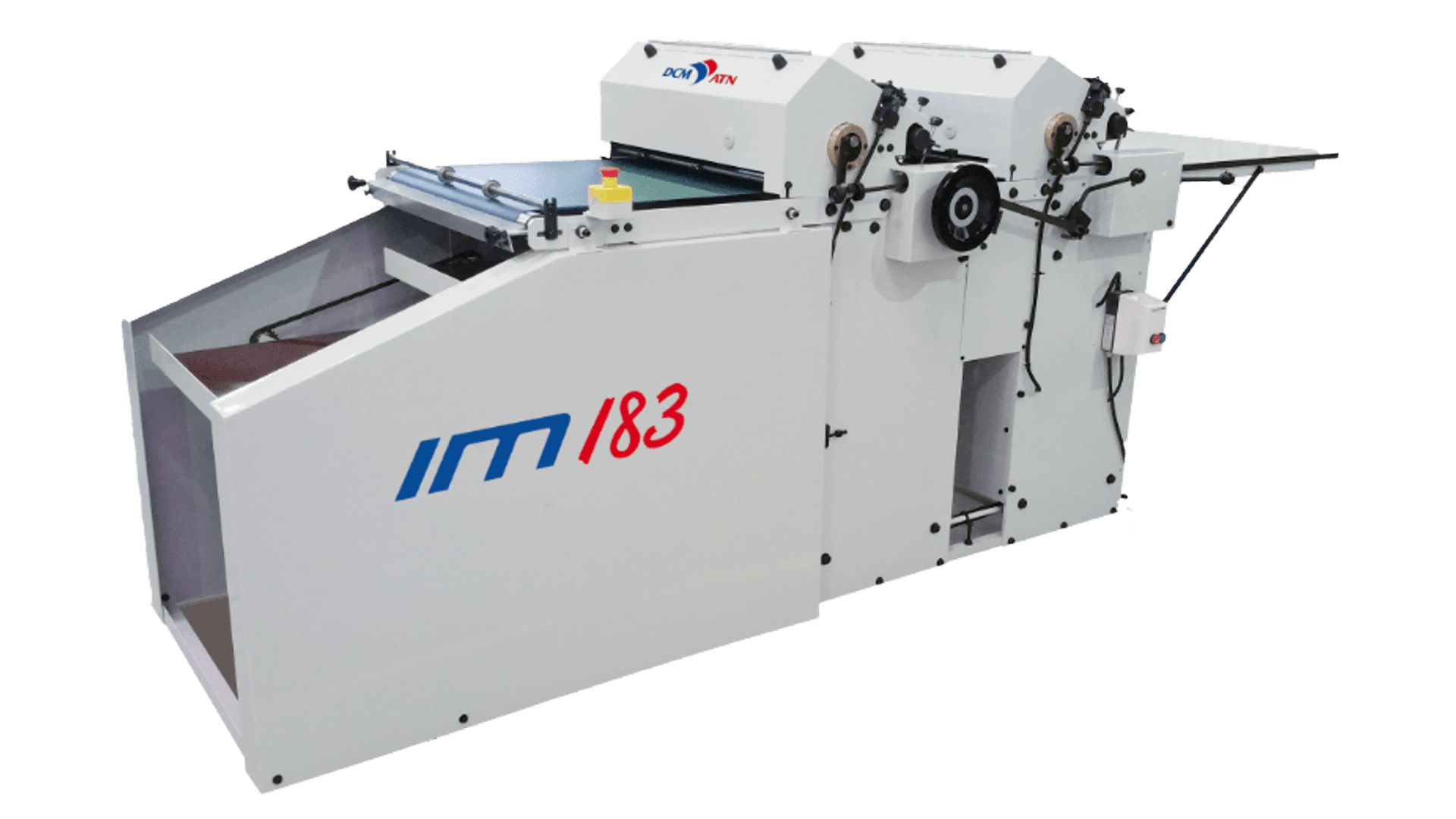

Here's a list of typical substrates used in flexographic printing:
- Paper
- Plastics
- Self adhesive media
- Carton board
- Corrugated board
The properties of each substrate impact both print quality and adhesion. The smoother the crisper the image will be and the artwork can be much more fine detail.
4. Common applications
Flexographic printing's versatility and efficiency make it suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries. Here's a more detailed look at some of the common and diverse uses of flexographic printing:
Flexible packaging
Flexographic printing is widely employed in the flexible packaging industry, where it excels in producing eye-catching, durable packaging solutions for a variety of products. Some specific applications include:
- Food packaging: Flexible packaging materials like plastic films and pouches are commonly used for packaging food products. Flexography ensures vibrant graphics and barrier coatings for preserving freshness.
- Snack bags: The production of snack bags, including potato chip bags and stand-up pouches, often relies on flexographic printing to create appealing packaging with excellent shelf presence.
- Beverage labels: Many beverage labels, particularly those on bottles and cans, are printed using flexography to withstand exposure to moisture and varying temperatures.
Labels and tags
Flexographic printing's high-speed capabilities and ability to adhere to various substrates make it an ideal choice for producing labels and tags across different industries. Key applications include:
- Product labels: From cosmetics to consumer goods, product labels require detailed graphics and vibrant colours. Flexo printing provides the precision and quality needed for these applications.
- Barcodes and QR codes: Flexographic printing is commonly used for producing barcode labels and QR code stickers used in logistics, retail, and inventory management.
- Pharmaceutical labels: The pharmaceutical industry relies on flexography to produce labels for medication bottles, ensuring critical information remains legible.
Corrugated boxes
Flexographic printing is extensively used in the production of corrugated cardboard boxes and packaging materials for shipping and retail display purposes. Specific applications include:
- Shipping boxes: Most corrugated shipping boxes are printed using flexography, allowing for branding and product information to be applied directly to the packaging.
- Point-of-purchase displays: Corrugated displays found in retail environments often use flexographic printing to create eye-catching graphics and branding.
- Custom packaging: Flexography enables businesses to create customized packaging solutions tailored to their products and branding, enhancing their marketing efforts.
Newspapers and magazines
While digital media has gained popularity, flexographic printing still plays a significant role in the newspaper and magazine industry, primarily for high-volume print runs. Some key applications include:
- Newspapers: Flexo printing allows newspapers to be produced quickly and cost-effectively in large quantities, meeting daily distribution demands.
- Magazines: High-quality magazines, including catalogues and brochures, benefit from flexographic printing's ability to produce large volumes with speed and efficiency.
- Inserts and supplements: Flexography is used to print inserts and supplements that are often included in newspapers and magazines, offering advertisers a cost-effective way to reach a broad audience.
Flexographic printing's adaptability and cost-efficiency continue to drive its application in diverse industries, making it a valuable choice for businesses seeking high-quality printed materials for their products and promotional materials.
5. Environmental impact
Environmental sustainability plays a role in todays printing industry, including printing. The flexographic printing process is adapting to adopt eco practices and minimize its impact on the environment. Lets delve deeper into whats changing for the better.
More sustainable practices
- Recycled substrates: One of the most significant steps towards sustainability in flexographic printing is the use of recycled substrates. These can include recycled paper, cardboard, and plastics, reducing the demand for virgin materials and conserving resources.
- Minimized waste: Adopting practices that minimize waste is crucial. This includes optimizing job layouts (nests) to reduce material waste, recycling scrap materials, and responsible disposal of waste inks and chemicals.
- Energy-efficient equipment: Using energy-efficient printing equipment and technologies can significantly reduce energy consumption during the printing process. Modern flexo presses often incorporate energy-saving features and automation.
- Water-based inks: Transitioning to water-based inks is a sustainable choice, as they have a lower environmental impact compared to solvent-based inks. Water-based inks emit fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and are less harmful to both the environment and workers' health.
Eco-friendly inks & substrates
- UV-curable inks: UV-curable inks are gaining popularity in flexographic printing due to their environmentally friendly characteristics. These inks cure instantly under UV light, resulting in reduced energy consumption and emissions.
- Low-VOC inks: Low-VOC (Volatile Organic Compounds) inks emit fewer harmful chemicals into the atmosphere, contributing to improved air quality and reduced environmental impact.
- Recyclable packaging: Flexographic printing plays a crucial role in the production of recyclable packaging materials, aligning with the growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions. These materials can be collected and recycled, reducing landfill waste.
- Eco-friendly substrates: The use of eco-friendly substrates, such as biodegradable films and papers, supports sustainability goals. These substrates break down more easily in landfills, reducing their environmental impact.
- FSC-certified materials: Many businesses seek printing on Forest Stewardship Council (FSC)-certified paper and cardboard, ensuring that the materials used in their packaging or printed materials come from responsibly managed forests.
Waste reduction & recycling
- Plate recycling: Recycling or reusing flexographic printing plates can help reduce waste in the printing process. Some photopolymer plates are recyclable, reducing the environmental impact.
- Ink recycling: Ink recycling programs enable the responsible disposal and potential reuse of leftover inks, reducing waste and minimizing the environmental footprint of ink disposal.
- Solvent recovery: Implementing solvent recovery systems can capture and purify solvents used in the printing process, reducing solvent waste and emissions.
- Efficient cleaning practices: Proper cleaning and maintenance procedures can minimize the use of cleaning chemicals and reduce their environmental impact.
Flexographic printers are placing emphasis on embracing practices and utilizing eco friendly materials to meet the rising need, for environmentally conscious printing solutions. By taking into account these factors flexographic printing can play a role, in fostering a printing industry that is more mindful of the environment and socially responsible.
6. Future trends
There are a few key trends in flexo printing and the printing press itself. Let's take a look at them.
Advancements in plate technology
There is amazing progress in developing plate materials to enhance print quality and prolong the lifespan of plates.
They're also getting quicker & easier to produce, meaning they can happen closer to the printing press, helping to speed up lead times.
Integration of digital tech
Variable data printing, colour management and speeding up the plate making process are all key focuses for suppliers to the industry.
For example, inline spectrophotometers help to measure the colour and ensure incredible accuracy.
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, this in-depth guide has provided a comprehensive understanding of flexographic printing, a versatile and adaptable printing process that continues to play a vital role in various industries. Flexography's efficiency, speed, and ability to print on diverse substrates make it a valuable choice for businesses seeking high-quality printed materials.
We have explored its key principles, pros & cons, delved into the intricacies of the flexographic printing process from prepress to post-press, and examined the materials used, colour management, common applications, and environmental considerations.
As flexographic printing evolves to meet the demands of a changing world, environmental sustainability remains a paramount concern. The adoption of eco-friendly practices, recycled materials, and responsible ink and chemical management is shaping the future of this printing method.
Whether you are a printing professional or an individual looking to understand the intricacies of flexographic printing, this guide has equipped you with valuable knowledge to navigate the world of flexography effectively. By staying informed about the latest trends, embracing best practices, and considering the environmental impact, you can maximize the potential of this dynamic printing technology while contributing to a more sustainable and eco-conscious industry.